[Curr Biol] Interplay between Cell Wall and Auxin Mediates the Control of Differential Cell Elongation during Apical Hook Development
[Curr Biol (2020) 30:1733]
Highlights
• The cell wall component xyloglucan is required for differential growth
• Xyloglucan deficiency perturbs cell wall mechanics and polar auxin transport
• Auxin response factor ARF2 mediates in interplay between cell wall and auxin
Summary
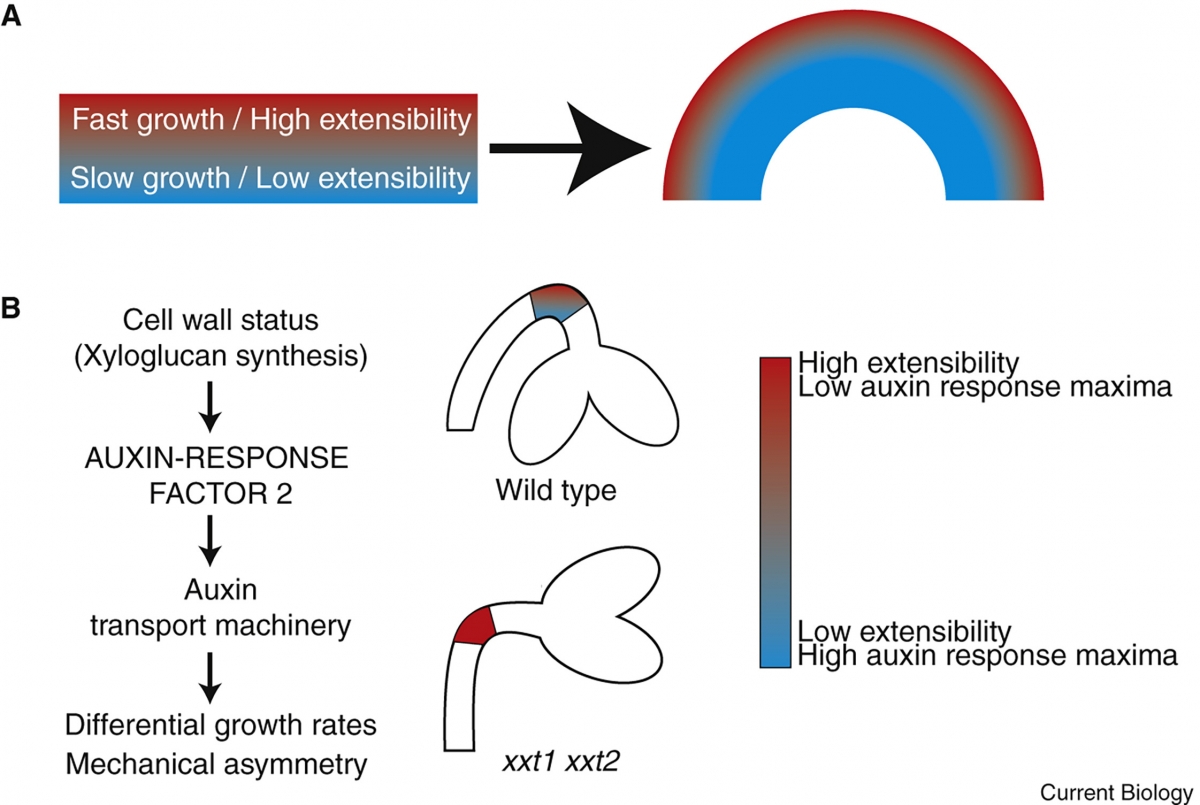
Differential growth plays a crucial role during morphogenesis [1, 2, 3]. In plants, development occurs within mechanically connected tissues, and local differences in cell expansion lead to deformations at the organ level, such as buckling or bending [4, 5]. During early seedling development, bending of hypocotyl by differential cell elongation results in apical hook structure that protects the shoot apical meristem from being damaged during emergence from the soil [6, 7]. Plant hormones participate in apical hook development, but not how they mechanistically drive differential growth [8]. Here, we present evidence of interplay between hormonal signals and cell wall in auxin-mediated differential cell elongation using apical hook development as an experimental model. Using genetic and cell biological approaches, we show that xyloglucan (a major primary cell wall component) mediates asymmetric mechanical properties of epidermal cells required for hook development. The xxt1 xxt2 mutant, deficient in xyloglucan [9], displays severe defects in differential cell elongation and hook development. Analysis of xxt1 xxt2 mutant reveals a link between cell wall and transcriptional control of auxin transporters PINFORMEDs (PINs) and AUX1 crucial for establishing the auxin response maxima required for preferential repression of elongation of the cells on the inner side of the hook. Genetic evidence identifies auxin response factor ARF2 as a negative regulator acting downstream of xyloglucan-dependent control of hook development and transcriptional control of polar auxin transport. Our results reveal a crucial feedback process between the cell wall and transcriptional control of polar auxin transport, underlying auxin-dependent control of differential cell elongation in plants.

위 논문의 간단 요약 정리입니다.
Xyloglucan 생성 mutant에서 cell elongation 및 hook development 관련 phenotype 확인
Cell wall의 작용을 이해하기 위해 cell elongation에 중요한 epidermal cells에서만 xyloglucan 생성을 회복시켜 봄 -> cell elongation이 회복됨을 확인 -> epidermal cell에서의 xyloglucan의 중요성 확인.
그 메커니즘을 이해하기 위해 mutants에서 auxin레벨을 분석함 -> auxin maxima가 손상된 것을 확인함. -> 그 이유를 이해하기 위해 auxin transporter의 localization을 확인했는데, 단백질 레벨이 낮아져 있을 것을 확인함. 이에 mRNA 레벨을 check하여 전사단계에서 조절됨을 확인함.
이과정을 매개하는 조절자로 ARF2를 추가적으로 밝힘.
그렇지만 cell wall 변화를 직접적으로 인지하여 세포 내부로 전달하는 key factor는 여전히 오리무중임 (수년내에 우리 랩에서 밝힐 수 있기를 희망함~!!!).