[PNAS] Collagen microarchitecture mechanically controls myofibroblast differentiation
[PNAS (2020) 117:11387]
Significance
Pathologic fibrosis is associated with altered collagen microarchitecture, but the functional impact of these changes on myofibroblast differentiation remains poorly understood. We experimentally and computationally analyzed the effect of collagen microstructure on matrix mechanics and determined its functional consequences on adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs), a cell type contributing to obesity- and cancer-associated fibrosis. Our findings highlight that collagen networks with thicker fibers and larger pores exhibit higher shear moduli than their similarly concentrated counterparts with thinner fibers and smaller pores. These differences promoted ASC mechanosignaling and consequential differentiation into α-smooth muscle actin-positive, contractile, and proangiogenic myofibroblasts. Insights from this work will advance the design of biomaterials for tissue engineering applications as well as antifibrotic therapies.
Abstract
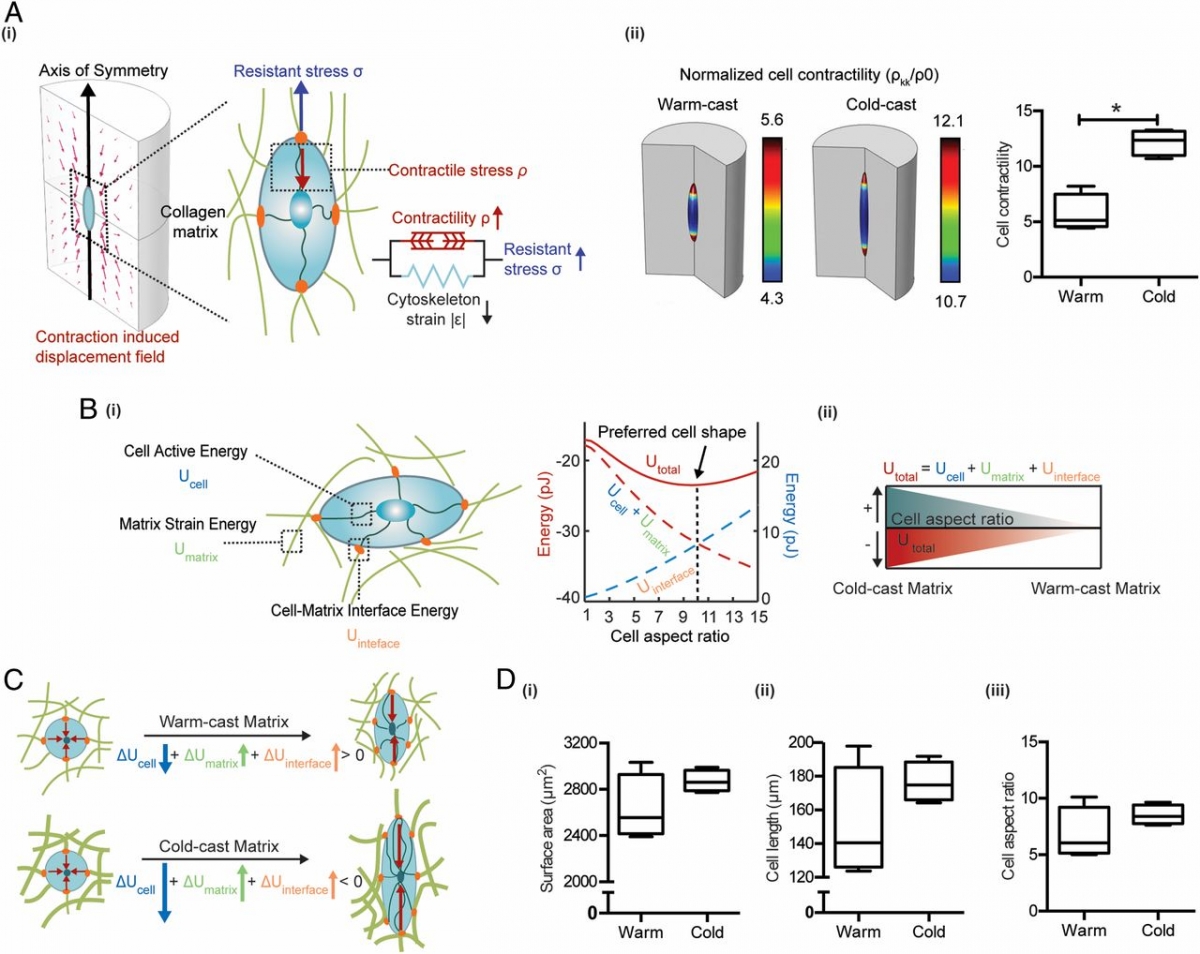
Altered microarchitecture of collagen type I is a hallmark of wound healing and cancer that is commonly attributed to myofibroblasts. However, it remains unknown which effect collagen microarchitecture has on myofibroblast differentiation. Here, we combined experimental and computational approaches to investigate the hypothesis that the microarchitecture of fibrillar collagen networks mechanically regulates myofibroblast differentiation of adipose stromal cells (ASCs) independent of bulk stiffness. Collagen gels with controlled fiber thickness and pore size were microfabricated by adjusting the gelation temperature while keeping their concentration constant. Rheological characterization and simulation data indicated that networks with thicker fibers and larger pores exhibited increased strain-stiffening relative to networks with thinner fibers and smaller pores. Accordingly, ASCs cultured in scaffolds with thicker fibers were more contractile, expressed myofibroblast markers, and deposited more extended fibronectin fibers. Consistent with elevated myofibroblast differentiation, ASCs in scaffolds with thicker fibers exhibited a more proangiogenic phenotype that promoted endothelial sprouting in a contractility-dependent manner. Our findings suggest that changes of collagen microarchitecture regulate myofibroblast differentiation and fibrosis independent of collagen quantity and bulk stiffness by locally modulating cellular mechanosignaling. These findings have implications for regenerative medicine and anticancer treatments.
